How to Check if Your System Supports USB Booting
- 1. What Is USB Booting and Why It Is Important
- 2. How to Check if Your System Supports USB Booting
- 3. Steps to Enable USB Booting in BIOS
- 4. What to Do If Your System Does Not Support USB Booting
- 5. Why You Should Use USB Booting for System Repairs and Installations
1. What Is USB Booting and Why It Is Important
USB booting allows you to boot your system from a USB drive instead of the internal hard drive. This is particularly useful for installing an operating system, running a live OS, or troubleshooting system issues when the primary operating system fails to load. For example, you can install Windows, run diagnostics, or recover files from a crashed system using a bootable USB drive.
Being able to boot from USB is essential for anyone who works with system installations or recovery tasks. If your system doesn’t support USB booting, it can limit your options for troubleshooting and OS installations. Knowing how to check and enable USB booting is crucial for managing your computer effectively.
2. How to Check if Your System Supports USB Booting
Before you start trying to boot from USB, you need to verify if your system supports it. Here’s how you can check:
- Check Your System's Specifications: The easiest way to check if your system supports USB booting is by looking at the system specifications. Most modern computers, especially those made after 2010, support USB booting. You can check the system’s manual or the manufacturer's website for information.
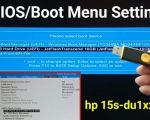
- Access BIOS/UEFI Settings: Reboot your computer and access the BIOS or UEFI settings. Typically, you can press the F2, DEL, or ESC key during the startup process (refer to your system's manual for the exact key). Once in the BIOS/UEFI, look for the Boot menu or Boot Order section.
- Check for USB Boot Option: In the Boot menu, check for any options related to USB drives. If you see options like "USB HDD" or "USB Storage Device," your system supports USB booting. If these options are not listed, your system may not have USB boot enabled, or it may not support it at all.
If you cannot find the USB boot option, you may need to enable it manually through the BIOS settings or refer to your system’s documentation for further guidance.
3. Steps to Enable USB Booting in BIOS
If your system supports USB booting but it is not enabled, you can easily enable it through the BIOS settings. Follow these steps:
- Enter BIOS/UEFI: Restart your computer and press the key to enter BIOS or UEFI settings (usually F2, DEL, or ESC during startup).
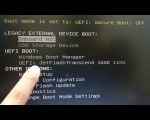
- Navigate to Boot Settings: Once inside the BIOS/UEFI, look for the "Boot" tab or a similar section that manages the boot order.
- Enable USB Boot: In the Boot options, enable the option for USB devices to appear in the boot order. It may be labeled as "Boot from USB," "USB HDD," or similar terms. Move the USB option to the top of the boot order list if needed.
- Save and Exit: After enabling USB boot, save your changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI settings. Your system will now recognize USB devices as bootable options.
Once USB booting is enabled, you can boot your system from a USB device by restarting the computer and selecting the USB device in the boot menu (usually accessed with the F12 key during startup).
4. What to Do If Your System Does Not Support USB Booting
If your system does not support USB booting, there are still a few things you can try:
- Use an External CD/DVD Drive: If your laptop or desktop has an optical drive, you can use a bootable CD/DVD to install the operating system or run recovery tools.
- Install a Bootable OS Using a Different Method: If USB booting is not supported, you can install an OS or perform system repairs using alternative methods, such as booting from a network connection (PXE boot) or using an internal drive if the system supports it.
- Update Your BIOS: Some older systems may not support USB booting by default but can do so with a BIOS update. Check the manufacturer's website for the latest BIOS version and update instructions.
While older systems may have limitations, there are often workarounds to help you perform installations or repairs effectively.
5. Why You Should Use USB Booting for System Repairs and Installations
USB booting offers numerous advantages when it comes to system maintenance, repairs, and installations:
- Portability: USB drives are compact and portable, making them easy to carry around and use on multiple systems for installations or repairs.
- Faster Booting: USB booting is generally faster than booting from traditional hard drives, especially if you're using a USB 3.0 drive or SSD.
- Versatility: USB booting allows you to run a variety of operating systems, troubleshoot system issues, and perform OS installations without the need for optical drives or network connections.
Using USB booting is an efficient and convenient way to manage your system’s software and hardware, ensuring that your computer stays up and running smoothly.
To learn more about USB booting and get the right tools for your system, visit Ninja Stik for solutions that can enhance your computer’s boot capabilities.