How to Go to Boot Menu: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 1. Understanding the Boot Menu
- 2. Importance of the Boot Menu
- 3. Accessing the Boot Menu on Different Devices
- 4. Boot Menu Options and Functions
- 5. Troubleshooting Boot Menu Issues
- 6. Using the Boot Menu for System Repair
1. Understanding the Boot Menu
The boot menu is a critical feature on your computer that allows you to choose which device or media the system should boot from. It is especially useful for troubleshooting, installing new operating systems, or running diagnostic tools. Knowing how to access the boot menu is essential for anyone who uses a computer regularly, as it can help you resolve various system-related issues.
1.1 What is the Boot Menu?
The boot menu is a list of devices that a computer can boot from, such as a hard drive, USB drive, CD/DVD drive, or network boot options. When you turn on your computer, it usually attempts to boot from the primary storage device (usually the internal hard drive), but by accessing the boot menu, you can select a different device to boot from.
1.2 Why Should You Know How to Access the Boot Menu?
Understanding how to access the boot menu can help you recover from system errors, perform installations, or run diagnostics when your operating system fails to load. It’s also useful when you need to boot from a bootable USB drive for system repairs or upgrades.
2. Importance of the Boot Menu
The boot menu plays a crucial role in troubleshooting and system recovery. It provides you with the flexibility to boot from different devices, which can be invaluable when facing hardware or software issues. By knowing how to use the boot menu, you gain access to advanced repair tools and installation options that might not be available otherwise.
2.1 Troubleshooting System Failures
If your operating system isn't booting correctly, the boot menu gives you the option to boot from a recovery disk, USB drive, or even network resources, helping you repair the system or recover important data.
2.2 Installing New Operating Systems
When installing a new operating system, the boot menu is essential for choosing the correct boot device. It allows you to boot from a USB drive or CD/DVD, where the installation files are stored, to begin the OS installation process.
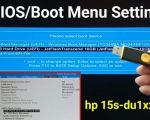
3. Accessing the Boot Menu on Different Devices
Accessing the boot menu can vary depending on your device's manufacturer and model. Here's how to access the boot menu on some of the most common devices:
3.1 Accessing the Boot Menu on Windows PCs
To access the boot menu on most Windows PCs, restart your computer and press a specific key, such as F12, F11, Esc, or F8, as soon as the manufacturer’s logo appears. The exact key depends on the manufacturer, so refer to your device's manual or look up the key specific to your model online.
3.2 Accessing the Boot Menu on Macs
On Mac computers, you can access the boot menu by holding the "Option" (Alt) key while turning on the computer. This will show you a list of available boot devices, such as your main hard drive or an external bootable USB drive.
3.3 Accessing the Boot Menu on Linux Systems
For Linux-based systems, the boot menu is often accessed by pressing the Shift key during boot, which opens the GRUB bootloader menu. From there, you can select the kernel or boot from a live USB to troubleshoot or install a new system.
4. Boot Menu Options and Functions
Once you access the boot menu, you’ll be presented with several options. These options allow you to choose the boot device or perform specific system-related tasks.
4.1 Selecting the Boot Device
The most common use of the boot menu is to select which device to boot from. If you want to boot from a USB drive or DVD, this is where you can select the appropriate device. Simply use the arrow keys to select the device you want to boot from and press Enter.
4.2 Accessing Recovery and Repair Tools
Many boot menus offer the option to access recovery tools, such as the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE), or the macOS recovery partition. These tools allow you to perform repairs, restore system backups, or reinstall your operating system if needed.
4.3 Network Boot Options
Some devices also provide the option to boot from a network. This can be useful for system administrators who need to perform network-based repairs or installations, or for using a network server to recover a system remotely.
5. Troubleshooting Boot Menu Issues
If you’re having trouble accessing the boot menu or booting from the desired device, here are some troubleshooting tips:
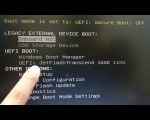
5.1 Check BIOS/UEFI Settings
If your boot menu doesn’t appear or your device isn’t booting from the correct device, you may need to adjust the boot order in the BIOS/UEFI settings. Enter the BIOS/UEFI by pressing the appropriate key during startup (usually F2, Del, or Esc), and adjust the boot priority to ensure your preferred boot device is selected.
5.2 Ensure Proper Bootable Media
If you're trying to boot from a USB drive or CD/DVD, ensure that the media is properly prepared and bootable. For USB drives, tools like Rufus can help you create a bootable USB, while tools like BalenaEtcher can help you create bootable DVDs.
6. Using the Boot Menu for System Repair
The boot menu is a powerful tool for system repair, allowing you to access recovery environments and restore or repair your operating system. Here’s how to use the boot menu for system repairs:
6.1 Using Recovery Mode
Both Windows and macOS provide built-in recovery modes that can be accessed through the boot menu. From these recovery environments, you can perform a system restore, reset your PC, or reinstall the operating system without losing your files.
6.2 Running Diagnostic and Repair Tools
If your system is experiencing issues such as slow performance or file corruption, many bootable USB drives and recovery tools include diagnostic tools to check for disk errors, fix corrupted files, or remove malware.