How to Troubleshoot BIOS Settings for USB Boot
- 1. Understanding BIOS Settings for USB Boot
- 2. How to Access BIOS Settings
- 3. Configuring BIOS for USB Boot
- 4. Common Issues When Booting from USB and How to Fix Them
- 5. Additional Tips for Successful USB Booting
1. Understanding BIOS Settings for USB Boot
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is the firmware responsible for booting up your computer before it loads the operating system. One of the key BIOS settings that users often need to adjust is the boot order, which determines from where the computer loads the operating system first. For instance, if you want to boot your computer from a USB drive, you will need to ensure that the USB drive is listed as the first boot device in the BIOS settings.
USB booting is a common practice when installing or repairing an operating system, running live environments, or recovering files from a malfunctioning system. To make this possible, you must configure the BIOS properly to recognize your USB drive as a bootable device.
2. How to Access BIOS Settings
Accessing BIOS settings typically happens during the boot-up process. Most computers prompt you with a key, such as F2, Del, or Esc, which you need to press as soon as the system starts. It is important to be quick because the window to enter the BIOS is often very brief.
Once inside the BIOS, you’ll find various tabs such as “Boot,” “Advanced,” and “Security.” Each of these tabs governs different aspects of your system’s performance. When troubleshooting USB boot issues, you should focus on the “Boot” tab, where you can set the boot priority. Here’s where you can make the necessary adjustments to allow booting from a USB device.
3. Configuring BIOS for USB Boot
To configure your BIOS for USB boot, follow these simple steps:
- Enter the BIOS settings by pressing the designated key during startup.
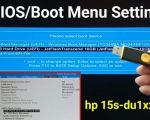
- Navigate to the “Boot” or “Boot Order” section. This may be labeled differently depending on the manufacturer of your motherboard or laptop.
- Locate the boot priority list and select “USB Drive” or “Removable Devices” as the first boot option.
- Save your changes and exit the BIOS. Your system will now attempt to boot from the USB drive.
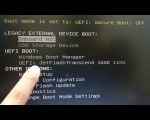
If you cannot find the USB option in the boot menu, it could mean that the USB drive is not recognized, or you might need to enable legacy boot mode or UEFI boot settings, depending on your system’s configuration. Some older systems require legacy mode to boot from USB, while newer systems may require UEFI mode for better compatibility.
4. Common Issues When Booting from USB and How to Fix Them
When troubleshooting BIOS settings for USB boot, several common issues may arise:
- USB Not Detected: If your USB drive isn’t showing up as a bootable option, check if it’s properly inserted or if the USB drive itself is bootable. Try the USB in another port or another computer to rule out hardware issues.
- Incorrect Boot Order: Ensure that the USB drive is set as the first boot device in BIOS. Double-check the boot priority list to make sure no other devices like the hard drive or network boot option are listed above the USB drive.
- Secure Boot Issues: Some systems have secure boot enabled by default, which can block USB booting. Disabling secure boot in the BIOS will allow the system to boot from the USB drive.
- Corrupted USB Drive: If the USB drive is not booting despite all settings being correct, it may have a corrupted operating system image. Try creating a new bootable USB drive using software like Rufus or the Windows Media Creation Tool.
5. Additional Tips for Successful USB Booting
Here are a few extra tips that can help you troubleshoot and ensure successful USB booting:
- Use High-Quality USB Drives: Low-quality or old USB drives may not perform well as boot devices. Consider investing in a reliable and fast USB 3.0 drive to improve performance.
- Check for BIOS Updates: Sometimes, BIOS updates can improve compatibility with USB booting. Check the manufacturer's website for your motherboard or laptop and update your BIOS if necessary.
- Enable Legacy Support: If you’re using an older USB drive, you may need to enable legacy support in BIOS, especially for systems using older BIOS standards (not UEFI).
- Test on Another Computer: If you’re still encountering issues, test the USB boot process on another computer to make sure the problem isn’t with your system configuration.