Understanding the Boot Menu in Laptops
- 1. What Is the Boot Menu in a Laptop?
- 2. How to Access the Boot Menu on Your Laptop
- 3. Common Boot Menu Options and Functions
- 4. Troubleshooting Boot Issues with the Boot Menu
- 5. Using the Boot Menu for System Repair and Recovery
1. What Is the Boot Menu in a Laptop?
The boot menu in a laptop is a pre-boot interface that allows users to choose the device from which they want the laptop to boot. Typically accessed during the startup process, this menu gives you control over how your laptop loads its operating system or other recovery tools. Whether you're booting from a USB drive, DVD, or hard drive, the boot menu provides quick access to these options.
Understanding the boot menu is especially useful for troubleshooting, system repairs, or installing new software. It allows you to bypass the default boot sequence and make the necessary adjustments for the task at hand.
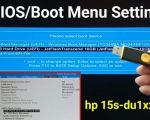
2. How to Access the Boot Menu on Your Laptop
Accessing the boot menu on your laptop varies depending on the manufacturer and model. However, the general steps are similar across most devices:
- Restart your laptop.
- Immediately press the appropriate key to enter the boot menu (this is often F12, ESC, or F2, but it may vary). You should see a prompt on the screen or refer to your laptop's manual for the exact key.
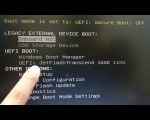
- Once the boot menu appears, use the arrow keys to select the device you want to boot from.
In some cases, the boot menu may automatically appear after pressing a key during the startup sequence. If it doesn't appear, you can enter the BIOS settings and enable the boot menu option from there.
3. Common Boot Menu Options and Functions
The boot menu typically provides several options, each designed to help you boot your laptop in different ways. Some common options include:
- Boot from USB: This option allows you to boot your laptop from a USB drive, which is helpful when installing or running an operating system from a flash drive.
- Boot from DVD/CD: You can boot your laptop from a CD or DVD drive, which is ideal for installing software or using recovery discs.
- Boot from Network: This option is often used in enterprise environments to boot a laptop over a network connection for system maintenance or deployment.
- Hard Drive: This is the default option, booting the laptop from the internal hard drive where the operating system is installed.
These options give you flexibility in how you manage and troubleshoot your laptop, especially if you're trying to recover or install a new system.
4. Troubleshooting Boot Issues with the Boot Menu
The boot menu can be invaluable when you're troubleshooting boot problems. If your laptop isn't booting properly, you can use the boot menu to try different boot devices or access recovery tools. Some scenarios where the boot menu can help include:
- Boot Device Not Found: If your laptop fails to recognize the boot device, you can manually select the correct device from the boot menu, such as a USB or CD drive.
- Operating System Issues: If your operating system isn’t loading correctly, using the boot menu can allow you to access repair tools or boot into safe mode.
- Corrupted Bootloader: The boot menu can help you select a bootable recovery disk or USB drive to repair a corrupted bootloader or restore your system from a backup.
By using the boot menu to access recovery tools or other devices, you can bypass startup problems and begin troubleshooting effectively.
5. Using the Boot Menu for System Repair and Recovery
The boot menu is not just for changing boot devices; it's also a powerful tool for repairing or recovering your laptop’s operating system. Many laptops include recovery options that can be accessed via the boot menu:
- System Recovery: Many Windows laptops offer a system recovery tool in the boot menu that allows you to repair or restore your operating system to a previous state.
- Restore from Backup: If you’ve made a system backup, you can use the boot menu to boot from the backup drive and restore your system to its original configuration.
- Safe Mode: The boot menu can help you boot into Safe Mode, where your system loads with minimal drivers and settings, useful for troubleshooting issues caused by installed software or drivers.
Using the boot menu for system repair and recovery can save time and effort when trying to resolve issues with your laptop, making it a vital part of laptop maintenance.