Everything You Need to Know About USB Device Boot
- What is USB Device Boot?
- How Does USB Booting Work?
- How to Set Up USB Boot for Your Device
- Common Issues with USB Boot and Troubleshooting Tips
- Real-World Examples of USB Device Booting
- Why Choose USB Booting for Your Devices?
What is USB Device Boot?
USB device boot is the process of booting a computer or other device from a USB storage device, such as a USB flash drive or external hard drive. Unlike booting from the device's internal hard drive, booting from USB allows you to run an operating system or recovery tools directly from the USB device without affecting the computer's internal storage. This method is popular for installing operating systems, running diagnostics, or using portable software setups without requiring installation on the host machine.
How Does USB Booting Work?
USB booting works by configuring the computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware to recognize a USB storage device as a bootable option. When the computer starts, the BIOS looks for bootable devices in a specific order (usually hard drive first, then CD/DVD, and finally USB). If the USB device is set as the primary boot device, the system will load the operating system or tools stored on the USB drive. This process requires the USB device to be properly formatted and contain a bootable image, such as an operating system or a live environment.
How to Set Up USB Boot for Your Device
Setting up USB boot on your device is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide:
1. Create a Bootable USB Drive
To begin, you need to prepare your USB device with a bootable operating system or recovery tool. You can do this using software like Rufus or the official Windows Media Creation Tool. Simply select the USB drive, choose the operating system you want to install, and let the software create the bootable USB.
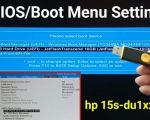
2. Enter BIOS/UEFI Settings
Next, restart your computer and access the BIOS or UEFI settings. This is typically done by pressing a specific key during startup, such as F2, F12, ESC, or DEL, depending on the manufacturer.
3. Change Boot Order
In the BIOS/UEFI settings, navigate to the boot menu and set the USB device as the first boot option. Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI.
4. Boot from USB
With the bootable USB plugged in, restart the computer, and it should boot directly from the USB drive. If everything is set up correctly, you’ll see the operating system or tool you installed on the USB, ready to use.
Common Issues with USB Boot and Troubleshooting Tips
While USB booting is a reliable method, there are a few common issues that users might encounter. Here are some tips to resolve them:
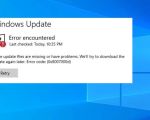
1. USB Drive Not Detected
If your computer doesn’t recognize the USB device as bootable, ensure that the USB is properly formatted and contains a bootable image. Also, double-check the BIOS/UEFI boot order to ensure that the USB drive is set as the first boot option.
2. Bootable USB Fails to Load
If the computer begins to boot from the USB but doesn’t load the system properly, try creating a new bootable USB using a different tool or ensure the image file is not corrupted.
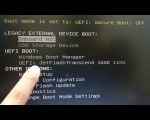
3. BIOS Settings Prevent USB Boot
Some newer computers with UEFI firmware may require you to disable Secure Boot in the BIOS/UEFI settings in order to allow USB booting. Be sure to check this setting if you're facing issues with booting from your USB device.
Real-World Examples of USB Device Booting
USB booting is commonly used in many scenarios, from personal computing to enterprise solutions:
1. Installing Windows from USB
Many users create a bootable USB drive to install or reinstall Windows on their devices. This is especially helpful when the device doesn’t have a CD/DVD drive or when you want a faster installation process.
2. Running Live Operating Systems
Another popular use of USB booting is running live operating systems. Linux users, for example, often boot into a live environment from a USB to try out different distributions before committing to an installation.
3. IT Professionals Using USB Recovery Tools
IT professionals often use USB devices to store recovery tools, antivirus software, or system repair utilities. With USB booting, these tools can be accessed directly, even if the computer's operating system fails to load.
Why Choose USB Booting for Your Devices?
USB booting offers several advantages that make it a valuable tool for both casual and advanced users:
1. Portability
One of the biggest benefits of USB booting is portability. You can carry your operating system, tools, and files on a single device and use them on any compatible computer.
2. Recovery and Repair
USB booting is an excellent way to recover or repair systems that fail to boot from their internal drives. You can use the USB to boot into recovery mode and troubleshoot the issue without needing to reformat the device.
3. Versatility
Whether you need to install an operating system, run diagnostics, or access data, USB booting gives you the flexibility to perform a wide range of tasks directly from the USB drive.